Home Care California | The Best Home Care Services
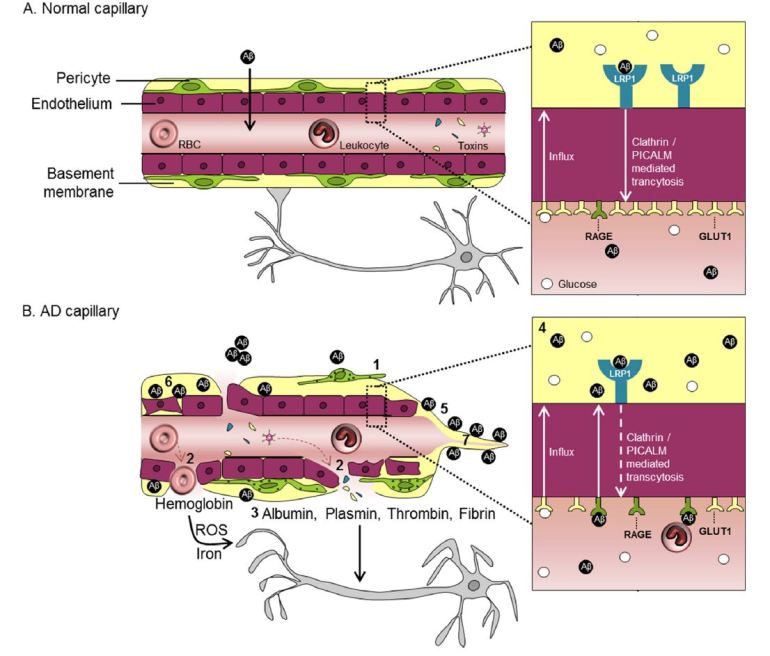 Blood–brain barrier (BBB) pathways to neurodegeneration in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
Blood–brain barrier (BBB) pathways to neurodegeneration in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
- A: In the normal capillary, there is an intact BBB composed of tightly joined endothelial cells and supported by mural pericytes, as shown in this simplified schematic. The BBB normally selectively regulates the passage of molecules from blood to brain and vice versa, and restricts entry of blood-derived products and toxins into the brain. There are many transporters and receptors along the BBB that permit molecules to cross the BBB via substrate-specific transport systems, some of which are particularly relevant to AD pathophysiogenesis, as illustrated in the graphics above. For example, the normal BBB has high expression of the glucose transporter (GLUT1),moderate expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1), and minimal expression of receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE).
Alzheimer’s Disease
- B: In the AD capillary, there is a vicious cascade of events that can lead to neurodegeneration…
View original post 1,416 more words
